The 4-2 volleyball rotation is the first offensive system beginner volleyball teams learn because of its simplicity.
This strategy involves using 2 dedicated setters who set only when they’re in the front court.
It gets its name ‘4-2’ since there’s 2 setters and 4 other players on court at once.
This is definitely one of the more basic strategies and is typically favored by beginners. It’s not really used by intermediate or advanced teams.
In today’s article we’re going to take a look at exactly how this formation works as well as discuss why you might choose this strategy over something like a 6-2 rotation or 5-1 rotation.

I’ve included diagrams as well as a printable PDF to make it easier to learn this strategy.
Let’s begin!
Advantages Of A 4-2 Rotation
First of all, why might you choose to run a 4-2 rotation? What are the primary benefits of using this approach over another?
It’s Super Simple
When it comes to movement around the court and where each player stands during serve reception, the 4-2 rotation is dead simple.
Rotations get complicated when you use back a back row setter which requires shuffling players around in order to move the setter closer to their base position.
But in the 4-2 rotation, we’re only ever using a front row setter which means there’s none of this added complexity.
This is why 4-2 is the best system to use with teams who have never played before. It allows players to get the hang of rotations without the confusion.
Improved Defense
In the 4-2 system, there’s always going to be 3 back row players who are concerned purely about defense.
In 5-1/6-2, the setter in the back row will often do a poor job defending against opposition spikes as they’re more concerned about transitioning into their base position so they can set the second ball.
When the back row setter is in their base position at the net, they can neither block nor dig effectively, meaning there’s effectively 1 less person on the court defensively.
Setter Can Be An Offensive Threat
This is usually considered a big advantage at higher levels because setters can dump the ball and make life very difficult for opposition blockers.
At the lower level, it can still be advantageous, particularly if you’ve got tall setters, but for the most part I’d actually consider this a disadvantage, since younger setters tend not to have the height/skill/athleticism to win points offensively.
Setter Is Always Close To Base
Since the setter is always in the front court, they’re basically going to stay in their base position the entire time.
This means there’s no scrambling to get from defense to base position; the setter is always going to be in a good spot to set the ball.
This is also an advantage on serve receive as it means teams can use all 5 other players to pass the ball if necessary.
Disadvantages Of A 4-2 Rotation
While the 4-2 rotation is quite popular amongst lower level volleyball teams, it’s definitely not perfect and certainly has some disadvantages, particularly for more experienced teams.
Only 2 Hitting Options Is Problematic
This is a really big issue at the junior level.
When your setter is front row, you can only set the outside or the middle blocker, which makes it very predictable and easy for opposition blockers to set up in the perfect position.
At higher levels, this is less of a problem since teams can use back row attackers, but less experienced teams don’t really have this option at their disposal.
In The 4-2 Rotation, Your Setters Have To Block
This isn’t necessarily a disadvantage, especially if you have tall, athletic setters.
But for teams with shorter setters, they might really struggle blocking effectively, as they’ll often be up against much taller outside hitters.
Volleyball 4-2 Rotation Diagrams
The following diagrams indicate where each player should stand on court during serve reception.
It’s important for teams to learn each of these rotations so that they’re able to move around the court efficiently and don’t make any rotational violations.
If you’re new to volleyball, be sure to check out my full guide to understanding volleyball rotations first.
There’s only 3 rotations to learn in the 4-2 system and it’s super simple…
4-2 Rotation Starting Positions
Below is the starting rotation of each player on court.
You’ll notice the players in the front row are colored in red whereas the back row players are in purple.
I’ve also chosen to use a libero in the back row in this diagram, although you could use another middle blocker in this spot.

It doesn’t really matter which positions each player starts in, so long as each of the setters, outsides, and middles/libero are opposite one another on the court.
We’ll start with the front row setter in position 4.
Also, in this article I’m just going to be discussing serve receive rotations. Make sure you check out my article explaining base positions in volleyball so you’ll know where to move once the ball has crossed back over the net!
Serve Receive Rotation 1 (Setter In 4)
In the first rotation, thesetter and OH will stand as close as possible to their base positions so they can switch around as soon as the ball is served.
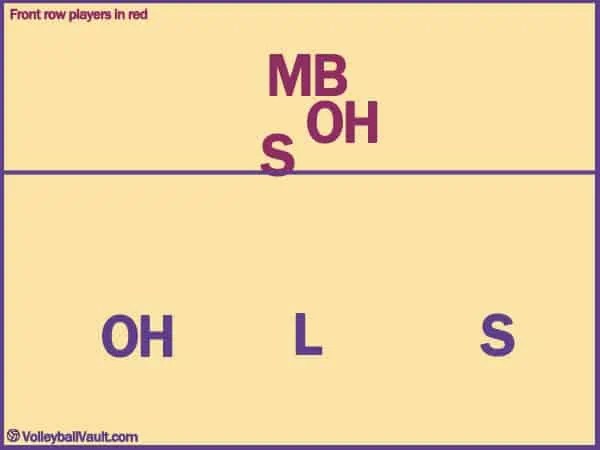
As soon as the ball is served, the setter will move to position 2 (to set the ball) and the OH will move to position 4 and transition out to get ready for offense.
Serve Receive Rotation 2 (Setter In 3)
In this rotation, all that really needs to happen is the setter and MB switch. The outside (who just came into the front row from the back court) can stay somewhere around the 10 foot line to get ready to spike.
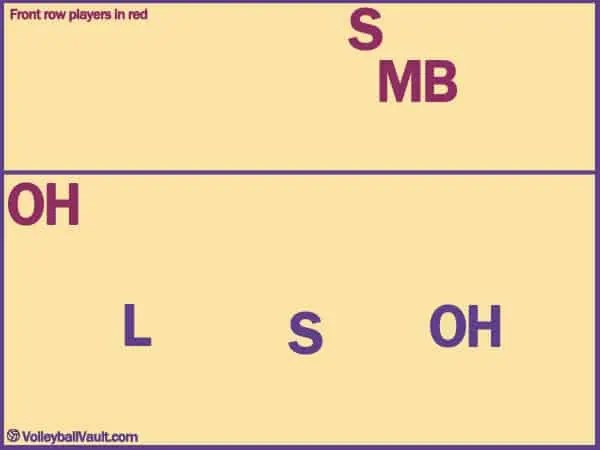
The MB will transition off the net to get ready to spike also.
If we need to shift our front row OH into the passing line up, we have that option also.
Serve Receive Rotation 3 (Setter In 2)
In the last rotation, the setter is already in their base position and the OH simply needs to stack to the right of the MB so they can quickly transition out to the left side of the court to get ready to hit.

After this rotation, our first setter will move into the back court and our back court setter will come into the front court.
At this point, we go back to the first rotation diagram and start all over again!
4-2 Volleyball Rotation PDF (Printable)
I’ve created a printable volleyball 4-2 rotation sheet which is just a single page PDF that contains the above diagrams.
Download Printable PDF
Feel free to print it off to give to your players as a cheat sheet to look over.
4-2 Vs 6-2 Volleyball Rotation
In the 4-2 system, both setters set from the front row.
In the 6-2 system, the setters only ever set from the back row.
There are other differences as well and I suggest taking a look at my 6-2 rotation write-up to get a better understanding of how these rotations differ.
4-2 Vs 5-2 Volleyball Rotation
A 5-2 rotation also has 2 setters, but 1 of them will always set from the front row and the other will always set from the back row.
The 5-2 is, as its name suggests, a perfect middle ground between 4-2 and 6-2.
It’s quite uncommon to see teams run a 5-2 offense, but it does make sense in certain circ*mstances.
How Do You Coach The 4-2 Volleyball Rotation?
The easiest way to teach the 4-2 rotation is to get your players on the court and simply walk them through each of the above rotations.

Practice having them move from the serve receive rotations into their defensive base positions and just slowly walk through each rotation as though it were a real game.
You could probably teach the entire 4-2 rotation in just 1 training session simply by slowly walking through it repeatedly for 20 minutes.
You could distribute the printable rotation sheet I’ve included above and have your players study it overnight, to help it sink in.
Run through it again at the start of the next training session and I’m sure your players will pick it up super quickly!
So long as your players understand what their base positions are, the 4-2 rotation is extremely quick to pick up.
4-2 Rotation FAQ
Below are some commonly asked questions I thought I’d take the time to answer.
Why is it called a 4-2 rotation?
It’s called a 4-2 rotation because there’s 2 setters and 4 attackers.
When using a libero of course it’s not quite going to be 4 attackers, but you get the idea.
Is there a libero in the 4-2 rotation?
Yes, teams can choose to use a libero to come on in the back court for the middle blockers.
At the junior level it’s quite common to see themiddle blockerplay through the back row, but if your team already has a dedicated libero then it makes sense to use them.
Do college volleyball teams run a 4-2?
No. You won’t really see 4-2 being used except for really young and inexperienced teams.